Diabetes Complication Mechanism
Diabetes Complications How Uncontrolled Diabetes Affects
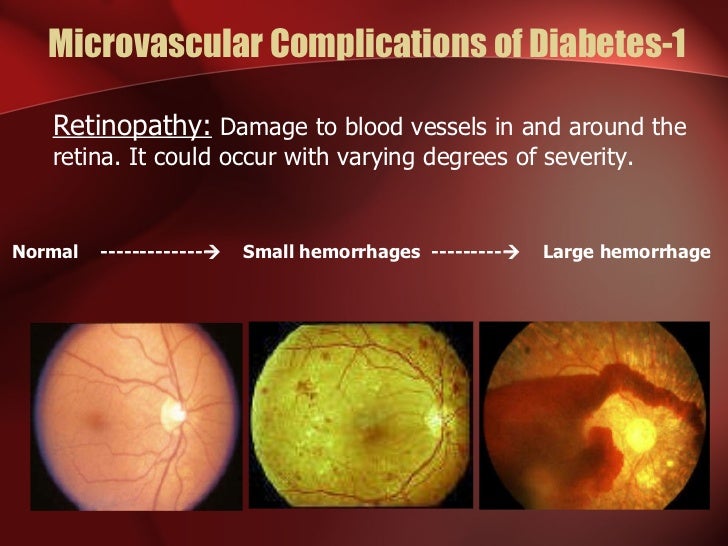
Diabetic retinopathy (dr) is a microvascular complication, which is considered as one of the main causes of visual impairment and blindness. dr-related glucose fluctuations can lead to the gradual onset of neurodegeneration and structural damage of the retina, ultimately causing blindness in patients with type 1 diabetes ( 18 ). Diabetes mellitus is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease which is the leading cause of death in the u. s. increasing prevalence of diabetes and diabetic atherosclerosis makes identification of molecular mechanisms by which diabetes promotes atherogenesis an important task. targeting common pathways may ameliorate both diseases. Mechanisms by which honey reduces diabetic complications. a look at fig. 2 reveals that honey can modulate hyperglycemia and oxidative stress to reduce diabetic complications. the author has proposed that targeting hyperglycemia and oxidative stress concomitantly is a better alternative to managing dm. 119 therefore, honey is a suitable agent. Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). if you.
Request pdf mechanisms of diabetic complications it is increasingly apparent that not only is a cure for the current worldwide diabetes epidemic required, but also for its major complications. Diabetes can damage this delicate filtering system. severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant. eye damage (retinopathy). diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), potentially leading to blindness. Diabetic ketoacidosis, a life threatening complication that affects people with type 1 diabetes. diabetic ketoacidosis occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin for glucose (blood sugar) to use for fuel. low insulin levels produce ketones (blood acids), which alters the body’s electrolytes. diabetic ketoacidosis can be fatal if not medically treated. Mechanisms of diabetic complications josephine m. forbes and mark e. cooper diabetes division, baker idi heart and diabetes institute, melbourne, australia; department of medicine and.
The Pathobiology Of Diabetic Complications Diabetes
1. physiol rev. 2013 jan;93(1):137-88. doi: 10. 1152/physrev. 00045. 2011. mechanisms of diabetic complications. forbes jm(1), cooper me. author information: (1)diabetes division, baker idi heart and diabetes institute, melbourne, australia. it is increasingly apparent that not only is a cure for the current worldwide diabetes epidemic required, but also for its major complications, affecting. A unified mechanism. over 13,000 articles published since 1966 seemed to show that all of these pieces of the puzzle were important in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications, yet two things suggested that something major was missing.
Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
But the most important ways to slow diabetes complications are to keep your blood sugar levels under control, eat right, exercise, lose weight, avoid smoking, and get high blood pressure and high. Gestational diabetes may also increase your risk of: high blood pressure and preeclampsia. gestational diabetes raises your risk of high blood pressure, as well as preeclampsia — a serious complication of pregnancy that causes high blood pressure and other symptoms that can threaten the lives of both mother and baby. Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels.
Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney diabetes complication mechanism failure in adults in the u. s. accounting for almost half of new cases. symptoms: you usually don't notice any symptoms with early diabetes-related kidney. Diabetes is a group of chronic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia. modern medical care uses a vast array of lifestyle and pharmaceutical interventions aimed at preventing and controlling hyperglycemia. in addition to ensuring the adequate delivery of glucose to the tissues of the body, treatment of diabetes attempts to decrease the likelihood that the tissues of the body are harmed by. Forbes jm(1), cooper me. author information: (1)diabetes division, baker idi heart and diabetes institute, melbourne, australia. it is increasingly apparent that not only is a cure for the current worldwide diabetes epidemic required, but also for its major complications, affecting both small and.
Hypoglycemia, or abnormally low blood glucose, is an acute complication of several diabetes treatments. it is rare otherwise, either in diabetic or non-diabetic patients. the patient may become agitated, sweaty, weak, and have many symptoms of sympathetic activation of the autonomic nervous system resulting in feelings akin to dread and immobilized pani. Diabetes is a result of your body’s inability to produce or use insulin. insulin is a hormone that allows your body to turn glucose, or sugar, into energy. In diabetic complications, experimental models have revealed a similar metabolic memory phenomenon to that seen in humans, which supports the diabetes complication mechanism postulate that there is a central role for epigenetic pathways, including modifications of histones. the potential effects of high glucose on these various epigenetic pathways is summarized in figure 7. Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications.
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic

Antidiabetic drugs (with the exception of insulin) are all pharmacological agents that have been approved for hyperglycemic treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus (dm). if lifestyle modifications (weight loss, dietary modification, and exercise) do not sufficiently reduce a1c levels (target level: ∼ 7%), pharmacological treatment with antidiabetic drugs should be initiated. known to have positive effect on many physical complications like diabetes and arthritis the cancerina is known for its Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or.
Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). More diabetes complication mechanism images. Pieces of the puzzle. the general features of hyperglycemia-induced tissue damage are shown schematically in fig. 1. the dcct (diabetes control and complications trial) and the ukpds (u. k. prospective diabetes study) established that hyperglycemia, shown on the far left of the figure, is the initiating cause of the diabetic tissue damage that we see clinically, shown on the far right (1,2).
of them can diminish the quality of life diabetes complications are primarily caused by 2 factors: excessive glycosylation process causes much of the damage in the complications of diabetes sorbitol accumulation sorbitol is the byproduct of glucose The aim of the present study was to characterize thermoregulatory mechanism in diabetes complication mechanism the feet depending on the lower limb diabetes complication (i. e. diabetic foot neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease or both) using a thermal camera. a transversal study was conducted to analyse the effect of diabetes complication on thermoregulation mechanism. this study was approved by the hospital of.
Diabetes symptoms and causes mayo clinic.

The pathobiology of diabetic complications diabetes.
Comments
Post a Comment